Impact of Urban Development on Georgia's Wildlife Conservation
Understanding Urban Development in Georgia
Urban development in Georgia has been on the rise, driven by factors like population growth and economic expansion. Cities like Atlanta are expanding rapidly, transforming landscapes and altering ecosystems. This growth often leads to the construction of homes, roads, and commercial spaces, which can disrupt natural habitats. As we embrace urbanization, it’s essential to consider how these changes affect local wildlife.
The environment is where we all meet; where we all have a mutual interest; it is the one thing all of us share.
With urban sprawl encroaching on natural areas, many species face habitat loss, which can threaten their survival. For instance, the gopher tortoise, a keystone species in Georgia, relies on specific habitats that are increasingly being developed. This not only affects the tortoise but also the myriad of species that depend on the same ecosystem. Understanding the dynamics of urban development is crucial for effective wildlife conservation.
Moreover, urban areas can introduce new challenges for wildlife, such as pollution, increased human-wildlife interactions, and road fatalities. As we build more infrastructure, we must find ways to mitigate these impacts to maintain biodiversity. Balancing growth with conservation is a challenge that requires collaboration among planners, conservationists, and the community.
The Effects of Habitat Loss on Wildlife
Habitat loss due to urban development is perhaps the most pressing issue facing Georgia's wildlife. When natural areas are replaced by buildings and roads, animals lose their homes and food sources, leading to population declines. For example, the red-cockaded woodpecker, an endangered species, has suffered from habitat fragmentation caused by development. This illustrates the direct link between human expansion and wildlife survival.
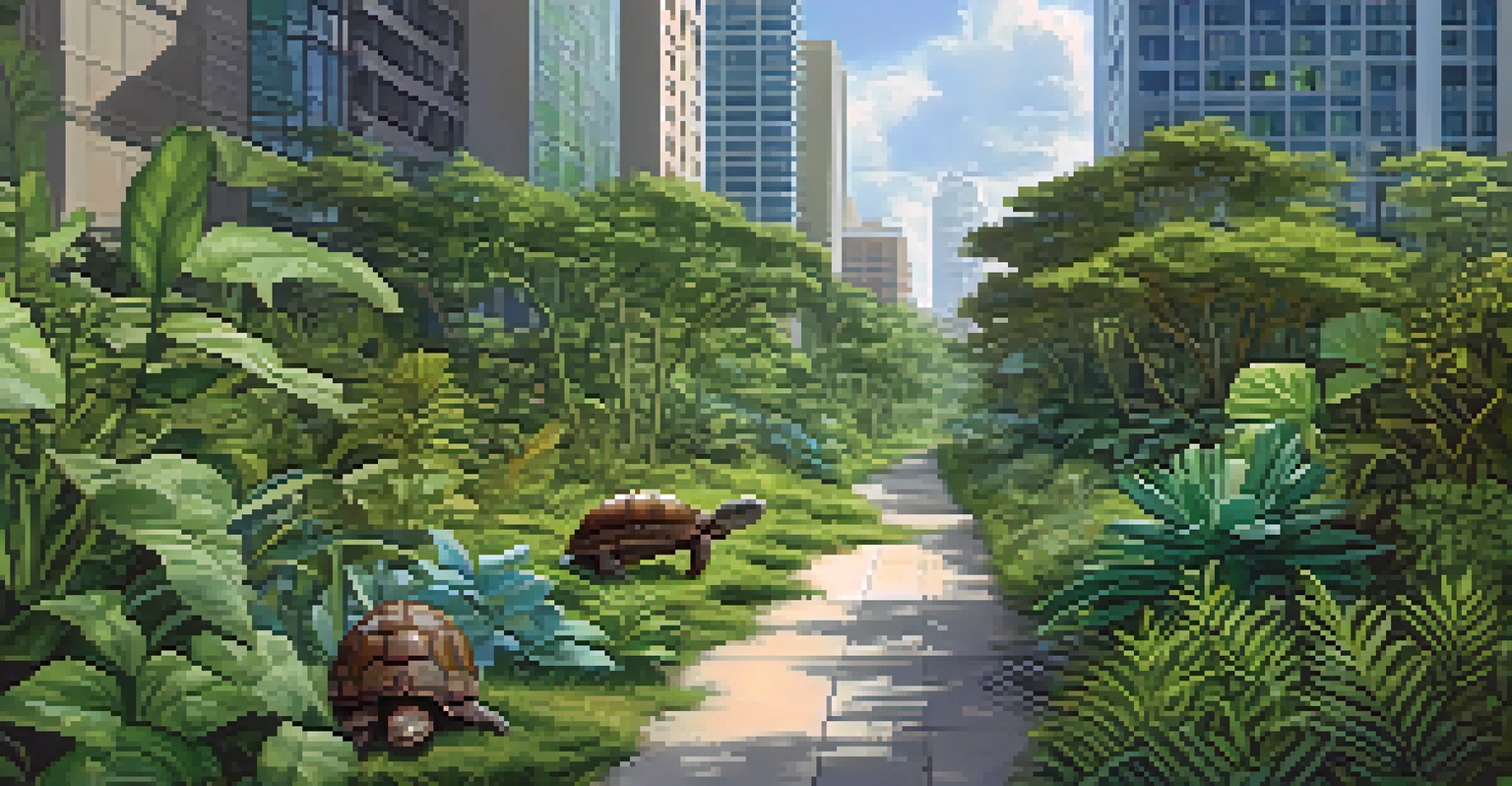

In addition to loss of habitat, urbanization can lead to habitat fragmentation. This occurs when large habitats are broken into smaller, isolated patches, making it difficult for species to find mates or resources. This isolation can result in inbreeding and decreased genetic diversity, further threatening species. For instance, smaller populations of the Eastern Indigo Snake are increasingly cut off from one another due to urban barriers.
Urban Growth Impacts Wildlife
Urban development in Georgia threatens local wildlife by causing habitat loss and fragmentation.
To combat these challenges, conservationists are advocating for wildlife corridors—designated areas that connect fragmented habitats. These corridors not only facilitate animal movement but also promote genetic diversity and resilience. By prioritizing habitat preservation and restoration, we can create a more sustainable coexistence between urban growth and wildlife.
Urbanization and Human-Wildlife Conflicts
As urban areas expand, encounters between humans and wildlife become more common, leading to conflicts. For example, deer populations in suburban areas can grow unchecked, resulting in vehicle collisions and damage to gardens. Such interactions often create negative perceptions of wildlife, prompting calls for population control measures that may not be ecologically sound.
The best time to plant a tree was twenty years ago. The second best time is now.
Moreover, urbanization can displace animals from their natural habitats, forcing them to adapt to human environments. Raccoons and coyotes, for instance, are becoming more prevalent in cities as they search for food. While these species can thrive in urban settings, their presence can lead to increased conflicts, such as scavenging or attacks on pets. Understanding these dynamics is essential for managing wildlife populations effectively.
Addressing human-wildlife conflicts requires a nuanced approach, focusing on education and coexistence strategies. Community awareness programs can help residents learn how to safely coexist with local wildlife, promoting tolerance and understanding. By fostering a sense of stewardship among urban residents, we can reduce conflicts and support wildlife conservation efforts.
The Role of Green Spaces in Urban Areas
Green spaces, such as parks and community gardens, play a vital role in supporting wildlife in urban environments. These areas provide critical habitats for various species, offering food, shelter, and breeding grounds. For instance, urban parks can serve as important stopover points for migratory birds, helping sustain their populations amid urbanization.
Additionally, green spaces can help mitigate some negative effects of urban development, such as heat islands and stormwater runoff. By incorporating native plants and trees, these areas can enhance biodiversity and improve overall ecosystem health. This not only benefits wildlife but also enriches the quality of life for urban residents, creating a more balanced environment.
Green Spaces Aid Urban Wildlife
Integrating green spaces in urban areas provides crucial habitats for wildlife and enhances biodiversity.
However, the challenge lies in ensuring that these green spaces are adequately preserved and connected. Urban planners and conservationists must work together to create a network of green corridors that allows wildlife to thrive even in densely populated areas. Investing in green infrastructure is crucial for maintaining biodiversity in urban settings.
Community Involvement in Wildlife Conservation
Community engagement is essential for successful wildlife conservation efforts in urban areas. Local residents can play a crucial role in monitoring wildlife populations, reporting sightings, and advocating for conservation measures. By fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility, communities can contribute significantly to preserving Georgia's wildlife.
Education initiatives can empower residents to become stewards of their environment. Workshops, nature walks, and citizen science projects can help individuals learn about local wildlife and the challenges they face. For instance, programs that teach people how to create wildlife-friendly gardens can increase habitat availability and support local species.
Moreover, collaboration between community members and local organizations can lead to impactful conservation projects. Whether it’s organizing clean-up days, planting native vegetation, or creating wildlife habitats, collective action can make a difference. Engaging the community is not just beneficial for wildlife; it fosters a deeper connection between people and nature.
Legislative Measures Supporting Wildlife Conservation
Legislation plays a crucial role in protecting wildlife amid urban development. In Georgia, various laws and initiatives aim to safeguard habitats and promote conservation efforts. For example, the Georgia Department of Natural Resources works to enforce regulations that protect endangered species and their habitats, ensuring that urban growth does not come at the expense of biodiversity.
Additionally, zoning laws can be leveraged to create buffer zones around critical habitats, minimizing the impact of urban sprawl. These regulations help maintain connectivity between habitats and mitigate human-wildlife conflicts. By prioritizing conservation in urban planning, we can create a framework that supports both development and wildlife preservation.
Community Involvement is Key
Engaging local communities in wildlife conservation efforts fosters stewardship and enhances habitat preservation.
However, advocacy is necessary to ensure that conservation measures remain a priority in legislative discussions. Residents and conservation groups must voice their concerns and push for policies that protect wildlife. By staying informed and engaged with local governance, communities can influence decisions that impact Georgia's wildlife conservation efforts.
Future Outlook for Wildlife Conservation in Georgia
The future of wildlife conservation in Georgia hinges on finding a balance between urban development and ecological preservation. As cities continue to grow, innovative solutions and collaborative efforts will be vital in ensuring that wildlife can thrive alongside urban populations. Integrating conservation principles into urban planning can lead to sustainable development that respects both nature and community needs.
Emerging trends, such as smart growth and sustainable architecture, offer promising avenues for minimizing the ecological footprint of urban development. Concepts like mixed-use developments and green building practices can help create urban environments that support both human lifestyles and wildlife habitats. By embracing these concepts, we can create cities that are more resilient and biodiverse.

Ultimately, the key lies in fostering a culture of conservation that values wildlife as an integral part of Georgia's identity. By prioritizing education, community involvement, and legislative support, we can pave the way for a future where urban development and wildlife conservation coexist harmoniously. This vision requires commitment and collaboration from all stakeholders to ensure that Georgia's rich biodiversity is preserved for generations to come.